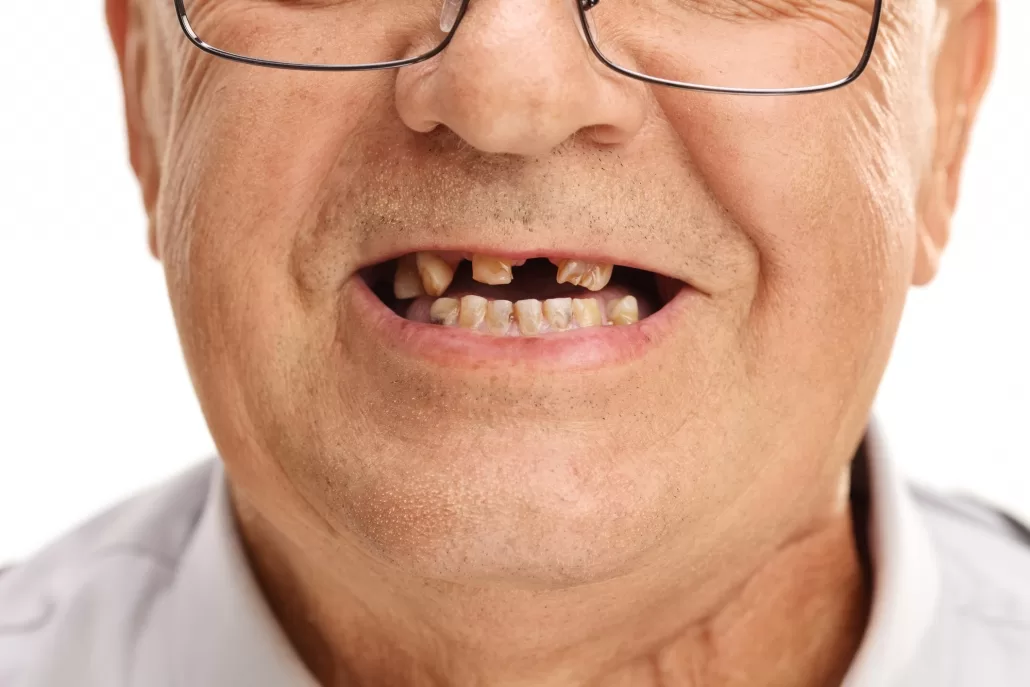
Oral hygiene is one of the most important measures to have a healthy mouth, teeth, and gums. Because the mouth is a primary entrance into the body, poor oral hygiene can have a negative impact on the whole body. Painful teeth, bleeding gums, and foul-smelling breaths are all signs of poor oral health. Bacteria can easily enter the bloodstream through the mouth, causing infection and inflammation. It is important to see your dentist regularly to make sure your body is in good health. In this part of moist health, there are some common and serious problems caused by oral health.
Complications of decayed teeth on cardiovascular diseases: Poor oral hygiene increases a person’s risk of heart disease. If the gums become inflamed due to bacteria that cause periodontal disease, these bacteria can enter the bloodstream and cause plaque and hardening. This hardening of the arteries is called atherosclerosis, which is very serious and causes problems with blood flow and heart blockage, and also increases the risk of a heart attack. It also has a detrimental effect on blood vessels and can lead to high blood pressure and stroke. It can also increase endocarditis, which is a dangerous and serious disease that occurs when the lining of the heart is infected.
Dementia from the effects of decayed teeth: Poor oral health also affects the brain. Substances released from inflamed gums by infection can kill brain cells and lead to memory loss.
Dementia, and possibly Alzheimer’s disease, can be caused by gingivitis, in which bacteria spread from mouth to canal and enter the bloodstream. Complications of decayed teeth in respiratory infections: The respiratory system can be damaged by poor oral hygiene, bacteria in the mouth from infected teeth, and swollen gums can enter the lungs, or enter through the bloodstream. These bacteria can lead to respiratory infections, acute bronchitis, and even COPD.
Diabetes due to complications of decayed teeth: Not only are people with diabetes more susceptible to infection, but periodontal disease and gum infections, in turn, increase diabetes and make it harder to control. Because gum disease and tooth decay raise blood sugar levels, people with poor oral health are at risk for diabetes.
Complications of decayed teeth during pregnancy: Oral hygiene is essential for pregnant mothers. Hormonal changes cause the infection to spread easily in the mouth. Any infection in a pregnant woman’s body increases the complications of pregnancy. These problems also cause premature birth. Tooth decay and gum disease put the mother and baby at serious risk.
Infertility and its relationship to decayed teeth: There is a close relationship between poor oral hygiene and infertility problems in women. Tooth decay and gum damage can affect the health of the whole body. People with poor oral health become pregnant and fertile later than other people.
Erectile dysfunction is a complication of decayed teeth: Having decayed teeth and poor dental and oral hygiene put men at high risk for erectile dysfunction. Bacteria from the patient’s gums and teeth can easily enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in the blood vessels; this inflammation can reduce or even stop blood flow. In these cases, an erection becomes more difficult or sometimes even impossible.
Cancer: It is obvious that poor oral hygiene practices, such as smoking or smoking, can lead to throat or mouth cancer. But there are other types of cancers that are associated with gum disease. The risk of kidney cancer, pancreatic cancer and leukemia is much higher in people with poor oral health.
Relationship between kidney disease and complications of decayed teeth: Chronic kidney disease is a serious health problem that affects the kidneys, heart, bones and blood pressure. Infections in the body, such as periodontal disease, can lead to kidney disease. In general, people with gum disease have an immune system. They are weak and are very likely to experience infection. Sometimes kidney disease can be very serious and even fatal.
Complications of decayed teeth and arthritis: According to the National Rheumatoid Arthritis Association, people with gum disease are four times more likely to develop arthritis. Both diseases are co-inflamed. Oral bacteria caused by gingivitis can increase inflammation throughout the body.